
Introduction about Training:
In a world of fast-changing regulations, rapidly advancing technology, and dynamic markets, it is essential to keep staff up to speed with developments in technology, standards, and regulation. People who are given proper training and support in their professional development are likely to be more motivated, proud of their position and responsibilities, and more skilful, knowledgeable, and productive.

1.SAFETY -HUMAN WELL BEING
- a) What is safety training:
Safety training describes the set of activities aimed at providing workers with the knowledge and skills to perform their duties safely and effectively. This type of training seeks to inform persons of the hazards and risks associated with various work activities and instructs them on how to identify, report, and address workplace incidents.
- b) Why safety training:
- Comply with the legal and regulatory requirement;
- Creating awareness about the surroundings;
- Reduce workplace stress;
- Use tools appropriately;
- Keep crisis exits which are easily accessible;
- Update about the unsafe conditions;
- Reduce Workplace Environment Stress;
- Wear the right safety equipment’s;
- c) What are the benefits of imparting training:
- · Reduce Accidents and Injuries;
- · To retain talent by creating confidence;
- · Make team more productive
- · Protect from litigation and reputation;
- · To save money;
- · Reduce Stress;
- · Encourage communication.
- d) Different Safety Training Modules:
| Sl. No | Training Topic | Duration | Inhouse/Remote |
| 1 | Construction Safety Training for supervisors | One Day | Both the options |
| 2 | Scaffolding Safety | One Day | Both the options |
| 3 | Work At Height | One Day | Both the options |
| 4 | Material Handling | One Day | Both the options |
| 5 | Welding, Grinding, Gas Cutting Safety | One Day | Both the options |
| 6 | Excavation and Trenching Safety | One Day | Both the options |
| 7 | Lifting & Rigging operations | One Day | Both the options |
| 8 | Lifting & Rigging operations | One Day | Both the options |
| 9 | Hazardous Material handling | One Day | Both the options |
| 10 | Lead Safety in the Workplace | One Day | Both the options |
| 11 | Personal Protective Equipment | One Day | Both the options |
| 12 | Use of Explosives | One Day | Both the options |
| 13 | Stairs and Ladders Safety | One Day | Both the options |
| 14 | Hand and Power Tools | One Day | Both the options |
- f) Who require Safety Training:
Managers, Supervisors and workers, it includes everybody in the organization.
- APPLIED 5S

5S is traditionally looked as a housekeeping technique. Very few organizations like Toyota used 5S beyond just housekeeping. If implemented with right spirit, 5S becomes the foundation for Business Excellence Journey. Many organizations mis-interpreted 5S as just a beautification tool. They do 5S whenever customer visit is planned or during top management visits. 5S should be linked to Quality, Cost, and Delivery. A true 5S avoids lot of quality issues thereby reduces the load on improvement projects!. Many shop-floor problems are the results of poor 5S.
Over and above all this, 5S can be used to create improvement and team culture in the organization. To differentiate with traditional 5S, we renamed it as Applied 5S. Our innovation team put all the learnings together in this program to demonstrate the power of 5S. We hope this will help you in your journey to become world-class.
a)What is applied 5S
A method of creating a lean and orderly workplace that exposes waste and in-efficiencies and makes abnormalities immediately visible;
IS Sort-(Seiri): -To remove what is not needed and keep what is needed.
2S – Set in Order/ Systematic arrangement (Seiton): Place things in such a way that they can be easily reached whenever they are needed. Keep only minimum quantity at the point of use;
3S -Shine (Seiso)- Keep things clean and polished; no trash or dirt in the workplace “don’t clean, keep it clean” “Cleaning with meaning”
4S-Standardize (Seiketsu)- Establish Standards for 1st 3S (1S,2S, and 3S) Use Visual methods to expose waste and abnormalities;
5S-Sustain through Self Discipline(Shitsuke)– Sustain through continuous training & Self Discipline. Make 5S as a Culture.
- b) Why Implement 5S
- It is a culture-building tool;
- It is the foundation for excellence;
- It is simple but powerful and everyone can understand easily;
- It can be applied to all Industries and Institutes;
- It can be applied at home;
- Children can apply it at schools.
- c) What benefits 5S can and brought to business:
- 10,000 sq feet of space released after effective 1S activity, which was converted into a training center – Mfg industry;
- Any Document/tool retrievals in less than 30 seconds by anyone – Service Industry;
- Equipment Breakdowns reduced by 50 % due to effective cleaning and maintenance by the employees;
- Employee discipline/punctuality improved;
- Productivity improved by 15 % after implementation of 5S pledge in a garment Industry;
- Quality issues due to the mix-up, confusions, wrong identification are completely eliminated;
- Auditors – Customers, potential customers impressed with the workplace enabling organization for new business;
- Employee engagement improved significantly and helped in cultural transformation
- d) Applicable to:
It can be applied in Warehouse, construction, retail, pharmaceuticals, chemical, paper and pulp, glass, ceramic, steel, cement, Schools, colleges, hospitals, diagnostic centers, libraries, and IT companies;
- e) Approach:
- Formation of Core team and defining roles and responsibilities;
- Zone formation in Shop floor and identifying Zone leaders;
- Training Core team members on 5S;
- Training 100 % employees on 5S by core team using local language;
- 1S and 3S workshop;
- Clearing of all RED tag items;
- Development of 5S Standards Manual;
- 2S and Visual Management Implementation-Model Zones;
- Horizontal deployment of 2S and Visual Management in all zones;
- Disposal of all items on using RED tag method and necessary approvals;
- 5S Auditor selection and Training;
- First Audit of 5S in all zones by core team;
- Initiate formal Audits (every month);
- Introduce Rewards and Recognitions;
- Continual improvements through Kaizens, Visuals, Kanbans, etc.,
3) TPM (TOTAL PRODUCTIVE MAINTENANCE)
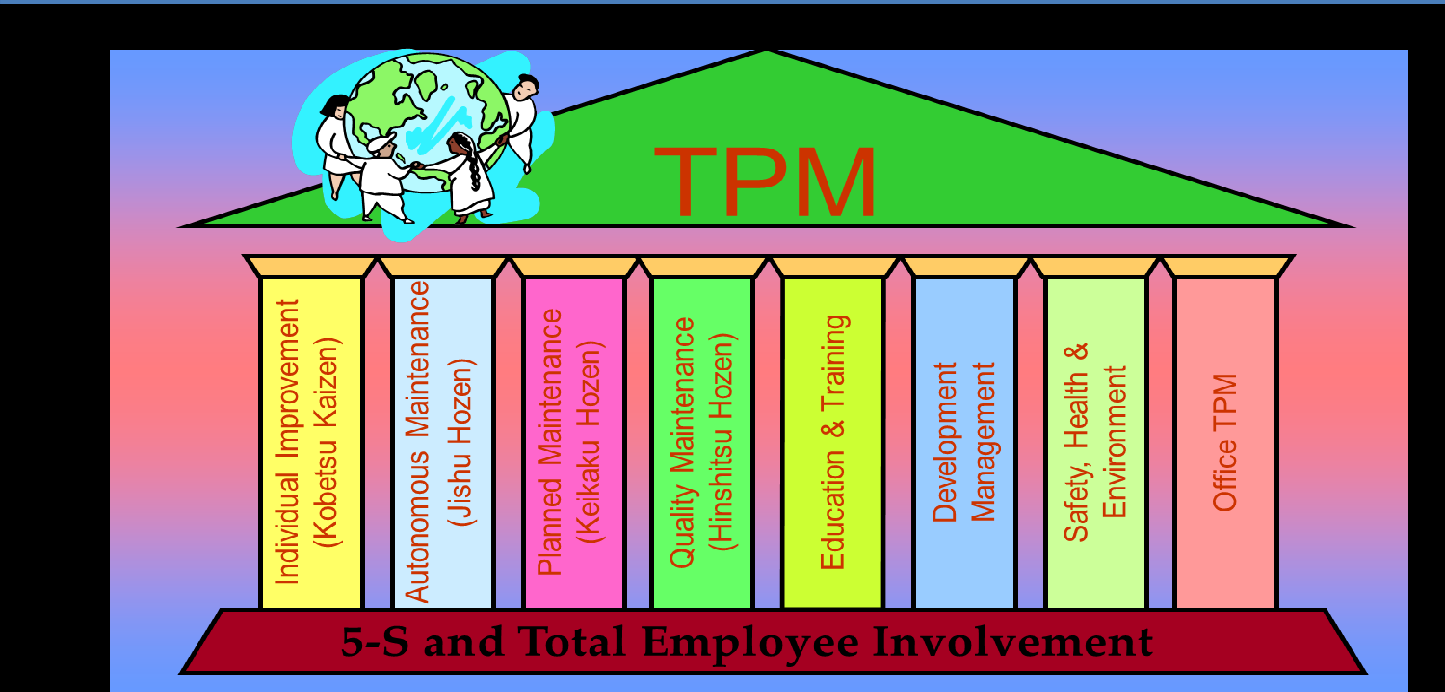
TPM is a maintenance philosophy aimed at eliminating production losses due to equipment status, or in other words, keeping equipment in a position to produce at maximum capacity, the expected quality products, with no unscheduled stops. This includes:
- Zero breakdowns
- Zero downtimes
- Zero failures attributed to poor condition of equipment
- No loss of efficiency or production capacity due to this equipment
It is understood perfectly the name: total productive maintenance, or maintenance that provides maximum or total productivity.
- What is TPM (Total Productive Maintenance)
It can be considered as the medical science of machines. Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a maintenance program which involves a newly defined concept for maintaining plants and equipment. The goal of the TPM program is to markedly increase production while, at the same time, increasing employee morale and job satisfaction.
TPM brings maintenance into focus as a necessary and vitally important part of the business. It is no longer regarded as a non-profit activity. Down time for maintenance is scheduled as a part of the manufacturing day and, in some cases, as an integral part of the manufacturing process. The goal is to hold emergency and unscheduled maintenance to a minimum.
- Why TPM (Total Productive Maintenance)
- Avoid wastage in a quickly changing economic environment;
- Producing goods without reducing product quality;
- Reduce cost;
- Produce a low batch quantity at the earliest possible time;
- Goods send to the customers must be non-defective.
- What benefits it (Total Productive Maintenance) brings to Business:
- Productivity improvement;
- Machine utilization;
- Defects reduction;
- Reducing unexpected breakdowns;
- Reduce accidents;
- Reduce consumable and spares cost.
- Applicable to:
Applied to all types of industries including Engineering, Service, Information Technology, Construction, Real Estates, Apparel, Healthcare, Hospitality, Education, Pharma and Process Industries.
- Approach:
- Preparing cation plan for TPM implementation;
- Identify an area for a pilot TPM program;
- Focus on restoring targeted equipment to prime working condition;
- Begin to measure Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE);
- Address Major Loss Causes;
- Implement proactive maintenance;
- Implement specific TPM concepts as needed.
- Different Training Modules:
| Sl. No | Training Topic | Duration | Inhouse/Remote |
| 1 | Quick Changeover (SMED) | One Day | Both Options |
| 2 | Poka-Yoke (Mistake Proofing) | One Day | Both Options |
| 3 | Statistical Process Control | One Day | Both Options |
| 4 | Basic Problem-solving tools and techniques | Five Days | Both Options |
| 5 | 8D and TOPS (Team Oriented Problem Solving) | Two Days | Both Options |
| 6 | Kaizen and Total Employee Involvement | Two days | Both Options |
| 7 | Awareness on Six Sigma | One Day | Both Options |
| 8 | Failure Mode and Effects analysis – FMEA | One Day | Both Options |
| 9 | Measurement System Analysis – MSA (R&R) | One day | Both Options |
4) LEAN SIX SIGMA YELLOW BELT
LSS Yellow belt Is a professional who is well versed in the foundational elements of the Lean Six Sigma Methodology, who leads limited improvement projects and/or serves as a team member as a part of more complex improvement projects lead by a Certified Green Belt or Certified Black Belt. An LSS Yellow Belt understands how to implement, perform, interpret and apply Lean Six Sigma in a skilled yet limited.
- Course Content;
- Lean & Six Sigma Overview
- COPQ (Cost of Poor Quality)
- DMAIC methodology introduction
- b) Introduction to DEFINE Phase
Problem selection and scoping tools
- Team formation, the definition of roles and responsibilities
- Problem and SMART Goal statements, Project Charter creation
- c) Introduction to MEASURE Phase
- SIPOC and “As Is” Process Mapping
- Introduction to 7 Wastes
- Introduction to Basic Statistics
- Use of Excel
- Measurement Systems Analysis
- Process Capability Study and Analysis, Sigma Level Calculation
- Basic 7 Tools of QC
- Introduction to ANALYZE phase
- Qualitative tools – C&E diagram, 5 Why analysis
- FMEA
- Graphical Techniques
- Lean Value Stream Mapping
- Introduction to Statistical Analysis
- Introduction to IMPROVE phase
- Solution priority Matrix
- 5S and Kaizens
- Lean tools – QCO /SMED & Kanban
- 3W1H
- Introduction to CONTROL phase
- Control Charts – Attribute and Variable
- Mistake Proofing (Poka-Yoke)
- Control Plans
- Case Studies
- Project Guidelines
- Test
- Who can attend this program:
Professional working in any manufacturing or service sector is eligible. Supervisors, Engineers, Asst Managers, and Managers, who is interested to solve industry problems.
- Certification:
All successful participants will be issued with a valid certificate of Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt.
5) ISO Management Systems

- Internal Auditor Training:
What is an Internal Audit (Quality, Environmental, Health & Safety, and Food Safety, etc.,)?
An internal audit is an important component to ensuring optimal performance of a management (Quality, Environmental, Health & Safety, Energy and Food Safety, etc.,) system. These audits can assist in monitoring the system and checking that it is meeting conformance and standards. The goal of an internal audit is to gather information about the effectiveness of the (Quality, Environmental, Health & Safety and Food Safety etc.,) system.
As the name implies, an internal audit is performed by someone within the company. However, the internal auditor should be associated with a different department than that which is being audited. The idea of an internal audit can be intimidating to some employees, so it is best to present these audits in a positive light, as a tool that will lead to improvement.
- Why Internal (Quality, Environmental, Health & Safety, Energy and Food Safety, etc.,) audits?
- Identify areas in need of improvement
- Employee growth
- Internal feedback
- Audit report
- Preparation for external audits
- What benefits these audits bring to the business:
- Improves the management of internal control within the organization
- Identifies gaps, non-conformances, and areas for improvement that can be used in internal strategic planning.
- Enable the business to become process-dependent rather than person-dependent
- Identifies inefficiencies in operational activities and provides action plans/recommendations to improve the overall efficacy of procedures.
- Serves as an Early Warning System, enabling deficiencies to be identified and remediated on a timely basis (i.e. before external, regulatory or compliance audits)
- Increases accountability within the organization.
- Satisfies the requirement of ISO management system standard
- Who can be trained on (Quality, Environmental, Health & Safety and Food Safety etc.,) Internal Auditor course:
- Senior management, QA managers, Executives, Production, Maintenance, HR, legal and Commercial professionals anyone interested in Quality management systems.
- Course Content:
- ISO 9001:2015 -Quality Management System Requirements;
- Auditing principles;
- Audit Terminology;
- Audit methodology;
- Auditing techniques;
- Responsibility of auditors, Auditee, and auditee management;
- Audit Checklist preparation, planning an internal audit
- Conducting an audit, NC writing, Correction and Corrective actions,
- Audit reporting.
- Certification
All successful participants will be issued with a valid certificate of Internal Auditor
- Deliverables:
- Guidelines of management system auditing according to ISO 19011:2011
- Application of auditing guidelines to ISO 9001:2015
- Initiating, preparing and conducting audit activities
- Preparing and distributing the audit report
- Completing audit and follow-up.
- Different Training Modules: Awareness & Internal Auditor
| Sl. No | Training Topic | Duration | Inhouse/Remote |
| 1 | ISO 9001: 2015-Quality Management System | 2 Days | Both the options |
| 2 | IATF 16949:2016-Automotive Quality Management System | 2 Days | Both the options |
| 3 | ISO 14001:2015-Enviroanmental Management System | 2 Days | Both the options |
| 4 | ISO 22000:2018-Food Safety Management System | 2 Days | Both the options |
| 5 | ISO 13485:2016-Medical Device Quality Management System | 2 Days | Both the options |
| 6 | FSSC 22000-FSSC-Food Safety System Certification | 2 Days | Both the options |
| 7 | BRC Food Safety Management System | 2 Days | Both the options |
| 8 | BRC Packaging Safety Management System | 2 Days | Both the options |
| 9 | ISO 27001:2022-Information Security Management System | 2 Days | Both the options |
| 10 | ISO 45001:2018-Ooocupational Health & Safety Management System | 2 Days | Both the options |
| 11 | ISO 50001: 2018-Energy Management System | 2 Days | Both the options |

